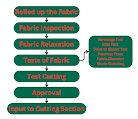
In garment production, finished dyed fabric is not always readily available. Often, fabrics need to undergo several preparatory processes before they are ready for garment manufacturing. These preparatory steps ensure the fabric is in the right condition for cutting, sewing, and finishing into high-quality garments. Below is an outline of the fabric preparatory process flow chart, detailing each step involved.
Flow Chart of Fabric Preparatory Process in Garments:
1. Dyed
and Finished Fabric in Roll
The fabric arrives after being dyed and finished, rolled up and ready for
inspection.
2. Fabric
Inspection
The fabric undergoes a thorough inspection to identify any defects, such as
color inconsistencies, holes, or tears, ensuring it meets the required quality
standards. This step is often carried out using the 4-point system, which helps
identify faults in the fabric or dyeing process. Proper inspection is crucial
for ensuring that only high-quality fabric is used in garment production.
3. Fabric
Relaxation
The fabric is allowed to relax and release any tension from the manufacturing
process. This step helps prevent shrinkage or distortion during the cutting
stage.
4. Different
Tests of Fabric
Several tests are conducted to check the fabric’s suitability for garment
manufacturing. Key tests include:
ü Shrinkage Test: Measures how much the fabric shrinks after washing.
ü GSM Test: Determines the fabric’s weight (grams per square meter).
ü Twisting: Assesses the fabric’s tendency to twist or distort.
ü Fastness Tests: Checks color fastness, light fastness, and wash fastness to ensure the fabric retains its color and quality.
ü Fabric Diameter: Measures the thickness of the fabric.
ü Shade Matching: Ensures color consistency across the fabric.
5. Test
Cutting
A small sample of fabric is cut to evaluate how it behaves when cut. This test
checks whether the fabric frays, distorts, or has any other undesirable
properties during the cutting process.
6. Approval
After all tests are completed, the fabric is reviewed. If it meets the required
quality standards, it is approved for production. Any fabric that fails to meet
the criteria may be rejected or sent for reprocessing.
7. Input
to Cutting Section
Once approved, the fabric is sent to the cutting section, where it is layered
and cut according to the garment pattern.
Key Tests in the Fabric Preparatory
Process:
® Shrinkage Test: To check how much the fabric will shrink after washing.
® GSM (Grams per Square Meter) Test: Measures the fabric's weight to determine its thickness and density.
® Twisting: Tests the fabric’s ability to maintain its form without twisting or distorting.
® Fastness Tests: These tests evaluate how well the fabric retains its color and integrity during washing, exposure to light, or rubbing.
® Fabric Diameter: Checks the thickness of the fabric to ensure it matches required specifications.
® Shade Matching: Verifies color consistency across the fabric to ensure uniformity in production.
By following this systematic flow, manufacturers ensure that the fabric is prepared to meet both functional and aesthetic requirements, leading to high-quality garments.


No comments:
Post a Comment